鎶椾綋 >> 鍏朵粬鎶椾綋
ATP5E铔嬬櫧鎶椾綋
|
浜よ揣鏈烔 1鍛?/span>
绱㈠彇璧勬枡鍙婃姤浠饵/span>
浜у搧浠嬬粛
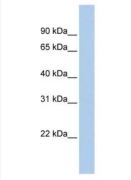
闈舵爣锛欬p style="text-indent: 2em;">ATP5F1E
浜у搧鍒悕锛欬p style="text-indent: 2em;">ATP5E锛 ATPE锛 MC5DN3锛 ATP5F1E锛 ATP synthase F1 subunit epsilon锛 ATP synthase F1 subunit epsilon锛 ATP synthase subunit epsilon, mitochondrial锛 ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, epsilon subunit锛 F(0)F(1)-ATPase锛 H(+)-transporting two-sector ATPase锛 mitochondrial ATP synthase epsilon chain锛 mitochondrial ATPase锛 ATP5E铔嬬櫧锛 鑳屾櫙淇℃伅锛欬div style="text-indent: 2em;">Mitochondrial ATP synthases (ATPases) transduce the energy contained in membrane electrochemical proton gradients into the energy required for synthesis of high-energy phosphate bonds. ATPases contain two linked complexes: F1, the hydrophilic catalytic core; and F0, the membrane-embedded protein channel. F1 consists of three Alpha chains and three Beta chains, which are weakly homologous, as well as one Gamma chain, one Delta chain and one e chain. F0 consists of three subunits: a, b and c. The e chain of F1 contains 50 amino acids and is the smallest of the five ATPase F1 chains. Mitochondrial ATPase e chain (ATP5E) localizes to the mitochondria and catalyzes ATP synthesis. 瀹夸富锛歊bt |
鐩稿叧浜у搧
|